Contact DFH Global Logistics for Best Rate
The Best Freight Forwarder in China
An updated Shipper’s Guide for China Custom Clearance
How to clear your goods with China’s Customs Service. DFH Global Logistics custom broker
If your plan is to engage in the importation and exportation of goods in and out of China, you need to be aware of the customs clearance procedures and documentary requirements involved in the entire process. Customs clearance can be done in any of the numerous custom offices in Mainland China. In this post, we will bring to your notice all you need to know regarding Chinese custom clearance to better help you prepare for the process.
1. What is Customs Clearance?
2. Custom Tariff Code
3. What is the Customs Clearance process
4. How to do Customs Clearance?
5. Documents required for import custom clearance
6. Documents required for export customs clearance
7. What is the Customs Clearance fee?
8. FAQs
Customs Clearance Procedure
The clearing of cargo in China involves a lot of procedures, and like what is obtainable in many other countries, customs clearance can pose a form of trade barrier to shippers largely due to a lack of transparency over tariff rates, trade licenses, and other complicated procedural processes.
If you want to avoid unnecessary delays at Chinese ports, it is crucial that you confirm before time, the standards your cargo must meet, and the necessary certifications required. Having the necessary documents and liaising regularly with your importer and custom clearing agent will help you avoid issues. Custom clearance are of three types namely,
- Air freightcustom clearance: This involves the clearing of cargo at airports.
- Sea freightcustom clearance: This involves the clearing of cargo at seaports
- Rail freight custom clearance: This involves the clearing of cargo at borders with international rail lines.
- Express freight custom clearance: All types of cargo handled by international courier companies are handled under express freight custom clearance.
At DFH Logistics, we specialize in handling the clearing of cargo on behalf of our clients from any of China's seaport, airport, or international rail lines. Our custom clearance solution handles express freight customs clearance, including clearance at the destination port. We have established an extensive operation in several countries, and the list keeps increasing. As of today, DFH Global Logistics handles custom clearance in China and these other countries.

We offer custom clearance services in:
Russia, India, Philippines, Singapore, Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia, Korea, Japan, Qatar, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Nigeria, Spain, Italy, France, Canada, Germany, UK, Netherlands, Turkey, Mexico, USA, Brazil, Egypt, Kenya, South Africa, New Zealand, Australia
What is Customs Clearance?
Customs clearance is a process that entails the processing and submission of documents required by customs authorities for the export or import of cargo into a country. The documents provided by the importer or exporter via their agents is what is used by the customs authorities to examine and assess the cargo in order to ascertain a duty payment figure. Before your cargo can be granted passage into or out of the country, you must fulfill the clearance requirements as established by the custom and excise laws of the country.
Custom Tariff Code
Due to the complex nature of custom clearance exercises and the long list of items been exported or imported into the country, shippers may have a hard time ascertaining the tariffs on their cargo. To make the process easy for shippers, custom authorities release tariff codes to the public, which is updated regularly. These codes are divided into sections, and each section accounts for one or more commodities.
- Section 1
Animal products and live animals
- Section 2
Vegetable products
- Section 3
Vegetable or animal fats and oils including cleavage items such as edible fats, vegetable or animal waxes
- Section 4
Processed foodstuffs, spirits, vinegar, beverages, tobacco and tobacco substitutes
- Section 5
Mineral items
- Section 6
Chemical and allied industry products
- Section 7
Plastic and rubber articles
- Section 8
Raw skins and hides, fur skin, leather, saddles, harness, travel items (handbags, similar containers), animal or silkworm gut, etc.
- Section 9
Wood articles, wood charcoal, cork articles, straw, basket articles, wicker articles, and other plating articles.
- Section 10
Wood pulp, other fibrous cellulose items, recovered waste and scrap items, paper and paperboard, and related articles.
- Section 11
Textiles and similar articles
- Section 12
Walking sticks, footwear, headgear, umbrellas, whips, seat sticks, riding crops, artificial flowers, prepared feathers, and human hair
- Section 13
Plaster, stone, cement, asbestos, mica, ceramic, glass and glassware
- Section 14
Cultured or natural pearls, precious and semi-precious stones, metals covered with precious metals, precious metals, coins, imitation jewelry.
- Section 15
Base metal and related articles
- Section 16
Machinery and their applications, electrical equipment, spare parts, sound recorders, image recorders and producers, their spare parts and related accessories.
- Section 17
Vehicles, vessels, aircraft, and associated transportation equipment.
- Section 18
Photographic, cinematographic, optical, measuring, checking, medical, surgical, precision equipment and appliances, clocks, watches, musical instruments, and their accessories.
- Section 19
Arms and ammunition and their parts or accessories.
- Section 20
Miscellaneous manufactured products
- Section 21
Work of art, antiques, and collector's pieces.
China HS Classification Code
China’s HS classification code is used to segment cargo into different classes, and each segment attracts a different customs clearance rate. As of August 1, 2018, Chinese customs added a new set of code numbers to the regular 8-digit to 10-digit HS codes. As an importer, before your cargo arrives at any of China’s ports, it is crucial that you classify your cargo in accordance with HS standards to determine the following:
- Tariff type: Tariffs are classified into various categories, namely, import duties, consumption tax, value-added tax.
- Declaration process: The customs declaration process for your cargo
- CIQ inspection: You need to determine the CIQ inspection and quarantine supervision if required for your cargo.
- Pre-market requirement: The authorities pre-market requirements and approval for your cargo.
Although one might argue that China’s HS code is in tandem with international conventions as it related to the description of Harmonized commodities, there is still quite a lot of differences with the Chinese model. These differences and the lack of a clear understanding of the codes are responsible for delays at the Chinese port of entry. If you apply for custom clearances in China with an incorrect HS code, delays are a possibility. Other causes of delays include
- Seized shipments
- Heavy fines
- A downgrade of company credit
- Importing cargo listed on the Monitoring list
- Smuggling and tax evasion
To avoid any of the above, you need a reliable custom clearing agent to handle the entire process, and DongFangHong Global Logistics can do that for you.
China Tariff Rates
The import and export tariff rates implemented by China changes from time to time in light of the dynamic regulations and policies initiated by the government. This means that how much you pay as Custom duty is never static but changes from time to time. It is also important to bear in mind that the tariff rates for imports are different from export rates. To be on a safe side, endeavor to contact the experts at DFH Global Logistics to provide you with an accurate tariff figure for your next shipment.
What is the Customs Clearance process
Whether you are importing goods into China or exporting goods out of China, there is a stipulated process you must follow to complete the exercise. If you abide by the approved clearance regulation, you should have no problems whatsoever. In a nutshell here are the quick steps to take
- First, run through the prohibited list to be sure that your cargo is not listed therein
- Consult the HS code to ascertain the accurate classification of your cargo
- Liaise with your clearing agent and supplier to arrange all the required documents pertaining to your cargo
- Hand over the documents along with the tariff fee to your custom clearing agents to handle the process
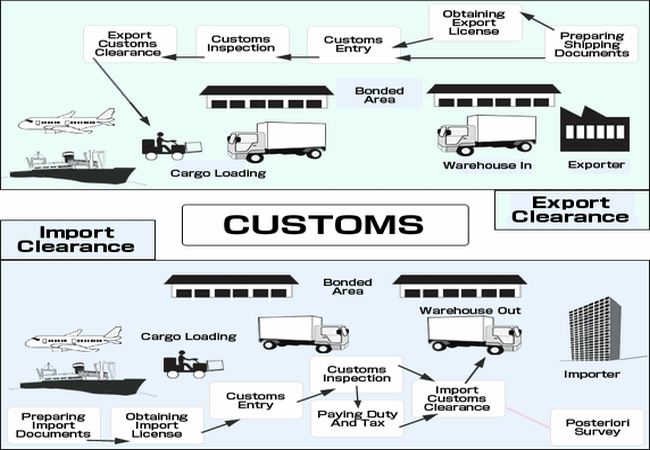
Taxes and Tariffs
Before you import or export goods into and out of China, make sure you have a clear idea about how much the current tariff costs. You can always consult your custom broker to furnish you with a figure. Now, you need to know that tariffs are basically divided into six different categories, and they are,
- MFN rates (Most favored nation)
- Tariff quota rates
- Preferential rates
- Agreement rates
- Provisional rates
- General rates
With DFH Global Logistics help, you can identify the category under which your shipment falls.
VAT
VAT is the duty charged on goods that are produced in the country. In some cases, importers pay VAT in addition to tariffs.
Excise Tax
Excise tax is a duty levied on special commodities such as wine, tobacco, and other ostentatious commodities like jewelry. Not all items attract excise taxes.
Custom Valuation
Along with all the other documents required by the authorities to complete the clearance process, a CIF document is also required. CIF stands for Cost, Insurance, and Freight and includes the normal price along with the packing cost, freight cost, insurance cost, commission to the seller.
China Customs Declaration Form
This form is another essential document. It is managed electronically, and the customs authorities have a guide that explains how to obtain and complete the form.
What is the CR number?
After registering your cargo with the Custom service, you will be allocated a Custom Registration code (CR). This code is issued to both importers and exporters and should be included in your customs declaration form.
China custom tracking
As an importer or exporter, you can also track your custom clearance status via the website of China’s customs service. To do your tracking, provide your declaration number and verification code.
How to do Customs Clearance?
Doing your custom clearance is quite easy if you have a reliable partner to provide you with expert support and logistics every step of the way. DFH Global logistics handles air and sea freight customs clearance as well as international parcel clearances. We also handle the following processes for clients:
- FedEx custom clearance
- DHL custom clearance
- TNT custom clearance
- Amazon custom clearance
- EMS custom clearance
- eBay custom clearance
- UPS custom clearance
Who is a Customs Broker?
A customs broker is a licensed individual or any entity that handles administration for importers and exporters of goods. Brokers submit appropriate documentation to custom authorities and use their wealth of experience to guide shippers in any area that has to do with the shipping process. Essentially, brokers act as an intermediary between the shippers and government agencies in the country.
Who is a Freight Forwarder?
A Freight forwarder is an expert who handles logistics and physical cargo transportation from the port of origin to the final destination. The freight forwarder liaises with custom authorities to ensure the movement of cargo from one point to another. They can also be custom brokers too, but not every custom broker is a freight forwarder. Freight forwarders operate on either the import or export side of the spectrum or both.
What is the difference between Freight Forwarders and Customs Brokers?
The differences are subtle, but there are certain responsibilities handled by one but not the other.
- Freight forwarders handle a wide range of responsibilities like logistics, warehousing, delivery and pick up service, etc. Custom brokers, on the other hand, handle service-specific duties involving custom agencies.
- Many freight forwarders can be custom brokers, but not every custom broker offers freight forwarding services.
- A Custom broker’s core focus is on the import aspect of an export transaction.
- Despite the difference, custom brokers and freight forwarders often work together to facilitate export transactions.
How long does Custom Clearance take in China?
The amount of time it will take to clear your cargo in China depends on several factors like port congestion issues, among other things. During summer months, when Chinese ports are full of cargo moving in or out of the country, it may take a little more time. Generally, Chinese customs officers visit different sites within the port during working hours to process and release items whose duties have been paid with adequate documentation. The process can take between 1-2 days or more depending on the season. Besides, port congestion, here are some factors that may cause delays.
- Unavailability of required shipping documents
- Incomplete shipping information
- A lack of description for the cargo
- A lack of Client Data file
Custom Clearance Documents
In this section, we will review the custom clearance documents required to process your cargo at seaports and airports. Without these documents, clearing your goods may prove to be a difficult exercise, if not impossible. For the purposes of clarity, we segmented the documents into two categories. Import custom clearance documents and export custom clearance documents.
Documents required for import custom clearance
- Bill of Entry
A bill of entry is a document filed by the importer of a cargo. It shows proof of the total value of outward remittances paid for the cargo. This document must be filed within a month of cargo arrival at the port of destination.
- Commercial invoice
A commercial invoice is used by customs officials to estimate the value of goods shipped into the country. With the information sourced from the commercial invoice, the customs official will be able to calculate the duty the importer should pay.

- Bill of Lading or Airway Bill
Bill of lading and Airway Bill are one and the same. A Bill of Lading is meant for cargo shipped in at seaports while an airway bill is for airports. This document is issued by the carrier, and it reveals the entire details about the cargo, including the delivery terms.
- Import License
Import licenses are required for special products. This license gives the bearer the legal right to ship in items that are highly regulated by the government. If you wish to import materials that fall under the list of regulated items, you need to apply for a license to do so. Once your goods arrive, custom officials demand this document for processing.
- Insurance Certificate
An insurance certificate is an evidentiary document supporting the importer's delivery declaration. This certificate helps the customs to ascertain whether the cargo has a selling price that is inclusive of insurance. Along with a commercial invoice, an insurance certificate is one of the documents used by the officials to determine the import duty charge.
- Letter of Credit
A letter of credit reflects all the terms and conditions agreed in the sale contract by the buyer and seller. A letter of credit is also a value assessment document submitted by the importer along with other documents.
Documents required for export customs clearance
- Pro Forma Invoice
A Pro Forma invoice signifies the intention of the exporter to sell a number of items at a predetermined price to the buyer or importer. It is generated based on the agreement of both parties to the transaction, and the exporters mail it to the buyer through any pre-agreed medium to complete the transaction.
- Custom Packing List
This is a list of all items contained in the shipment, and they are matched with the information available in the pro forma invoice. A custom packing list is pasted on the container detailing the port of destination so as to avoid shipping the container to a wrong destination.
- CO Certificate
A country of origin certificate is an exporter's declaration certifying that the goods about to be shipped have been produced and packaged in the country of origin.
- Customs Invoice
This is a mandatory document for all exports as it contains valuable information about selling price, product quality, packaging costs, weight volume, and product description. These details are what the custom authorities in the importing country use to assess the value of the consignment.

- Shipping Bill
A shipping bill is a report that serves as a sort of measuring record by custom authorities. To obtain a shipping bill, the exporter will have to submit the following documents.
- GR Forms
- Packing List
- Export License
- Indent
- Contract Acceptance letter
- Sale invoice
- Letter of Credit
- Purchase Order
- AR4
- Examination Certificate
- Port of Trust document
- Bill of Lading
An exporter’s bill of lading is the same as the one for importers. It provides information about the transport contract between the carrier and the cargo owner, along with other vital details concerning the cargo. A Bill of Lading is a very important document without which items cannot be cleared by customs.
- Bill of Sight
This is a declaration made by the exporter to the customs if the buyer (importer) is not 100% sure about the nature or quality of the items being shipped. This bill allows whoever is receiving the items to inspect them first before making custom duty payments. Bill of sight documents can act as a substitute if there is a lack of a bill of entry certificate.
- Letter of credit
Serves the same purpose for exports as it does for imports. It clearly states that the importer will pay the exporter an agreed sum at the completion of the transaction. A letter of credit is issued based on agreed contractual terms.
What is the Customs Clearance fee?
China Custom clearance fee is the sum total of money paid by shippers to custom agencies to clear their goods from the sea or airports. There are different types of custom clearance fees, as you will see below.
- Custom Duty
This is an indirect tax levied on items imported into a country. Some exported items also attract custom duty fees as well. If the duty is levied on an imported item, it is called an import duty. If it is levied on an exported item, it is called an export duty.
- Basic customs duty and additional custom duty
Basic customs duty is the standard duty levied on similar items while additional duties are levied on items aside from the basic duty depending on their volume, size, or quality.
- Excise and Custom Duty
Excises are similar to custom duty since they are both forms of indirect taxes levied on goods. The only difference between the two is that Excises are levied on items brought into the country via land borders.
- VAT
Value Added taxes are imposed on not only goods but also on services at different stages of production. VAT is an indirect tax levied on services or products produced in a country. Just like custom and excise duties, governments use VAT to generate revenue.
Calculating how much you have to pay as tax can be done with a customs tax calculator. But if you want to avoid miscalculations, the smart move will be to rely on the help of experts to value your items in order to ascertain an accurate figure. At DongFangHong Global Logistics, we help our clients to evaluate the correct amount their cargo will attract as custom taxes.

How much does a custom clearance cost?
The cost is hugely dependent on the nature of the items, the country of origin, the selling price of the item, and several other factors.
What is the custom charge in India on goods from China?
Charges vary depending on the product, but the basic duty may range between 7%-25%. You also need to include GST payments as part of the entire cost.
Who pays custom clearance?
The buyer or importer of the cargo is responsible for paying custom clearance, such as taxes, duties, and other general fees. These charges vary based on the selling price, volume, weight, and nature of the cargo. The buyer is also responsible for freight costs, packaging, and loading unless such a responsibility is transferred to the seller (exporter) under contractual agreements.
Who is responsible for customs clearance?
If you want to clear your goods, customs clearance and freight forwarding agent will handle the responsibility on your behalf. Freight forwarders, which also hold custom clearing licenses, process your documentation with the customs agency based on laid down rules and procedures. They also provide other miscellaneous services such as packing, loading and general sea, air, express, or rail freight logistics services.
Why choose DFH Global Logistics?
If you choose DFH Global Logistics to handle your China customs clearance, you are handling such a responsibility to an experienced establishment with the wealth of experience and expansive network to see the process through. We will make sure that the process is devoid of delays and also, we will provide you with timely feedback to put your mind at rest regarding the clearing status of your cargo.
We also offer logistics services from the pickup to the drop off point. With our help, you need not move a muscle since we will handle the entire exercise on your behalf. For any questions or inquiries, you may have concerning China’s Custom Clearance procedure, contact us today and let us be of help to you.
FAQs
- How to check your custom clearance status?
To check your custom clearance status, visit the Chinese custom website. Provide your verification code and your declaration number. If you have any more questions, please do reach out to us for help.
- How long does customs clearance take in the Philippines?
Several factors may influence waiting times, but on average, all imported articles take as long as 3-7 days to be cleared.
Contact DFH Global Logistics for Best Rate
Your Best Freight Forwarder in China

